What is Sequela?
Sequela is a condition that occurs as a result of a previous disease.
Teeth can be damaged or lost due to dental caries, trauma, erosion, attrition, and abrasion.
Teeth can be damaged or lost due to dental caries, trauma, erosion, attrition, and abrasion.
What is Dental Caries?
Dental Caries is the main cause of dental pain. Caries begins as a painless white spot (enamel decalcification, which may be reversible), followed by cavitation and brownish discoloration. When caries affects the dentine, discomfort may come from different atmospheric conditions or from sweet or sour food or drink.
So, Dental caries is defined as a complex, infectious, and transmittable oral illness that develops over time as a result of the complex interaction between cariogenic oral flora (biofilm) and fermentable food carbohydrates on the tooth surface.
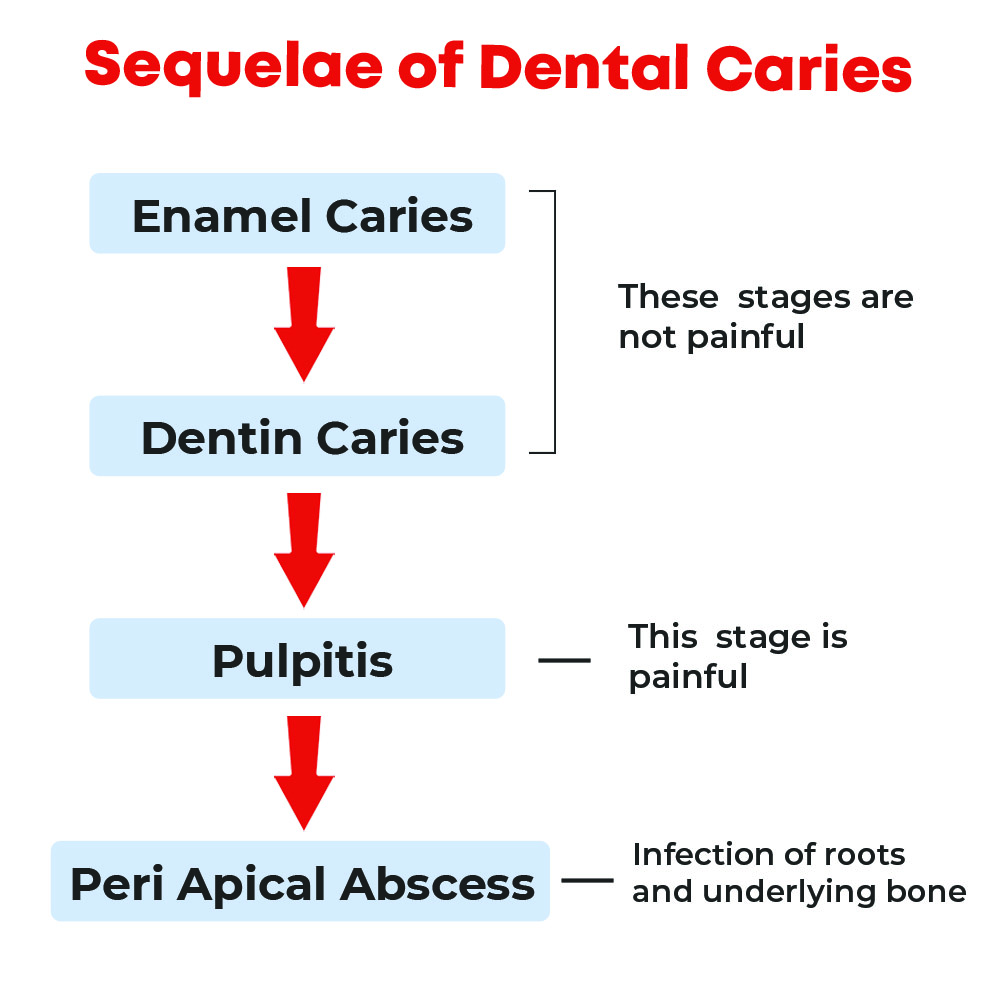
Untreated caries can spread through the dentine to the pulp, which becomes irritated (pulpitis). This inflammation causes severe, long-lasting pain within the boundaries of the pulp chamber (toothache). The pulp eventually dies due to inflammation. Inflammation can then extend around the tooth apex, causing an abscess, granuloma, or cyst.
So, Dental caries is defined as a complex, infectious, and transmittable oral illness that develops over time as a result of the complex interaction between cariogenic oral flora (biofilm) and fermentable food carbohydrates on the tooth surface.
Untreated caries can spread through the dentine to the pulp, which becomes irritated (pulpitis). This inflammation causes severe, long-lasting pain within the boundaries of the pulp chamber (toothache). The pulp eventually dies due to inflammation. Inflammation can then extend around the tooth apex, causing an abscess, granuloma, or cyst.
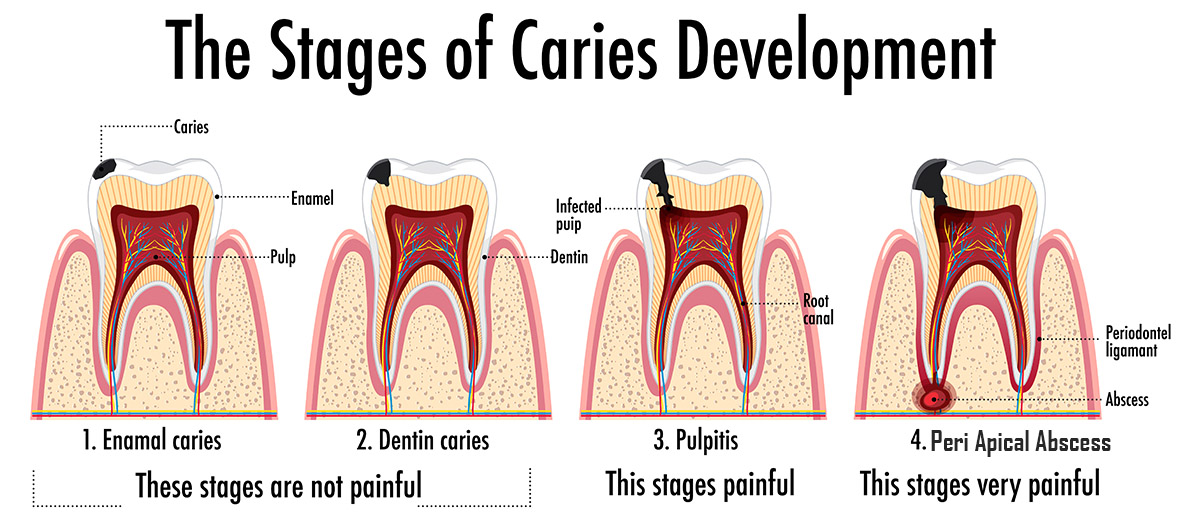
1. Enamel Caries (Changes in Enamel):
Caries begins as a painless white spot (decalcification of the enamel, which may be reversible), followed by cavitations and the emergence of brownish discolouration.
2. Dentin Caries
Dentin caries is termed active and “rapidly progressing“ when the dentin appears soft and wet, with a high bacterial load, notably of Lactobacillus species, whereas dentin with “slowly progressing“ caries is described as leathery, or hard and discoloured.
3. Pulpitis
Most common reason for dental pain.
The majority of cases of pulpitis are mostly brought on by dental caries, in which bacteria or their byproducts infiltrate the dentin and pulp tissue.
This causes severe, chronic pain inside the narrow confines of the pulp chamber, and the pulp eventually undergoes necrosis.
The majority of cases of pulpitis are mostly brought on by dental caries, in which bacteria or their byproducts infiltrate the dentin and pulp tissue.
This causes severe, chronic pain inside the narrow confines of the pulp chamber, and the pulp eventually undergoes necrosis.
4. Peri Apical Abscess (Infection of Roots & Underlying Bone)
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection. The abscess can form in many locations near the tooth for a number of reasons.
A periapical tooth abscess is frequently caused by an untreated dental cavity, an injury, or previous dental procedure.
A periapical tooth abscess occurs when germs reach the dental pulp. The pulp is the internal component of the tooth that contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue.
Bacteria enter the tooth through a dental cavity, a chip, or a fracture and spread all the way to the root. The bacterial infection may result in swelling and inflammation at the root’s tip.
A periapical tooth abscess is frequently caused by an untreated dental cavity, an injury, or previous dental procedure.
A periapical tooth abscess occurs when germs reach the dental pulp. The pulp is the internal component of the tooth that contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue.
Bacteria enter the tooth through a dental cavity, a chip, or a fracture and spread all the way to the root. The bacterial infection may result in swelling and inflammation at the root’s tip.
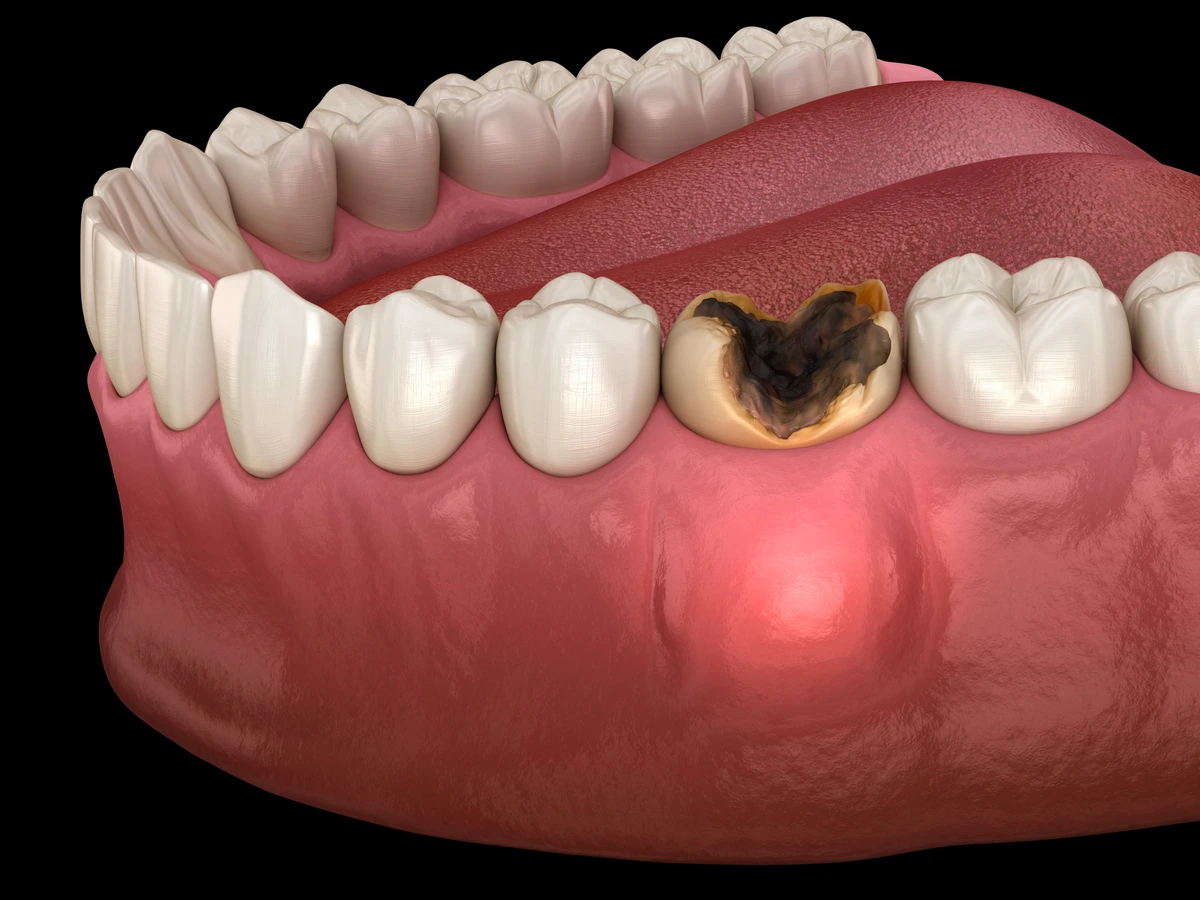
Common symptoms of dental caries
You may have dental caries symptoms all the time or only on occasion. Any of these dental caries symptoms can be serious at times.
Dental caries symptoms are often confined to the mouth. They consist of:
• Holes in the surface of a tooth
• Pain when chewing
• Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and beverages
• Toothache
Dental caries symptoms are often confined to the mouth. They consist of:
• Holes in the surface of a tooth
• Pain when chewing
• Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and beverages
• Toothache
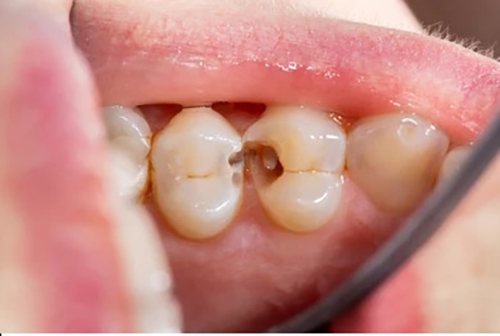
Causes of Dental Caries
Bacteria and harmful substances such as acid that come into touch with your teeth cause dental caries. After you eat, normal bacteria in your mouth interact with food remains and acids to form a sticky film known as plaque. If you don’t clean plaque on a regular basis with flossing and brushing, it can build up and harden into tartar.
Plaque and tartar, along with bacteria and acids, can erode the enamel on your teeth, resulting in dental caries, also known as cavities. Dental caries typically starts off as tiny, shallow holes; if left untreated, they can grow larger and deeper and can result in tooth loss or destruction.
Plaque and tartar, along with bacteria and acids, can erode the enamel on your teeth, resulting in dental caries, also known as cavities. Dental caries typically starts off as tiny, shallow holes; if left untreated, they can grow larger and deeper and can result in tooth loss or destruction.
Risk factors for dental caries
Dental caries is more likely to occur as a result of several circumstances. Not everyone at risk for dental caries develops it. Dental caries has several risk factors, including:
• Advancing age (older teeth form plaque more quickly)
• Dry mouth (inadequate salivation)
• Excessive consumption of sugary, starchy or acidic foods or drinks
• Poor dental hygiene
• Recessed gums
• Smoking
• Advancing age (older teeth form plaque more quickly)
• Dry mouth (inadequate salivation)
• Excessive consumption of sugary, starchy or acidic foods or drinks
• Poor dental hygiene
• Recessed gums
• Smoking
Prevention
Your risk of developing dental caries may be decreased by
• Limiting your intake of sugar, starch, and acid
• Avoiding foods that are sticky or could get stuck in your teeth (such as peanut butter or popcorn)
• Brushing your teeth twice a day is recommended.
• Flossing at least twice a day
• Fluoridation of the public water supply
• Visiting your dentist on a regular basis for routine cleanings and examinations
• Having dental sealants, or protective coatings, put on your teeth if your dentist recommends it
• Getting fluoride treatments from your dentist
• Seeking treatment for symptoms of dry mouth
• replacing sugar with artificial sweeteners
• Using antibacterial mouthwash
• Limiting your intake of sugar, starch, and acid
• Avoiding foods that are sticky or could get stuck in your teeth (such as peanut butter or popcorn)
• Brushing your teeth twice a day is recommended.
• Flossing at least twice a day
• Fluoridation of the public water supply
• Visiting your dentist on a regular basis for routine cleanings and examinations
• Having dental sealants, or protective coatings, put on your teeth if your dentist recommends it
• Getting fluoride treatments from your dentist
• Seeking treatment for symptoms of dry mouth
• replacing sugar with artificial sweeteners
• Using antibacterial mouthwash